
Exploring Generative AI and Bedrock
We’re excited to share insights into the features of Generative AI and Bedrock today, along with ways they can be applied to business services.
As an IT professional, I’m thrilled about AWS’s introduction of this service. In the early days, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) had steep barriers to entry. Understanding various AI frameworks, acquiring domain knowledge, and handling data collection and processing were daunting tasks requiring significant resources. Without ample time and manpower, these technologies felt out of reach.
Now, AWS Bedrock simplifies everything. With just API calls, we can achieve amazing results! It’s hard not to exclaim, “This is incredible!” Let’s dive into an overview to understand how it all works. Without further ado, let’s begin exploring!
Generative AI Trends and Large Language Models (LLMs)
The Future of AI Is Now

Before diving into the details, allow me a quick retrospective. Early digital transformation primarily focused on infrastructure upgrades—for example, moving on-premise systems to the cloud, implementing containerization, or integrating DevOps into workflows. However, the most significant game-changer has been Generative AI.
According to research, 95% of business analysts now view AI as critical to digital transformation. Additionally, 80% of organizations report utilizing AI in their business activities or production processes. It’s clear that AI adoption will continue to grow, revolutionizing enterprise workflows. Furthermore, 81% of businesses reported a positive return on investment within two years of implementing AI, highlighting its value in driving commercial outcomes.
AI Use Cases and Investment
Let’s look at findings from an IDC survey conducted in July:
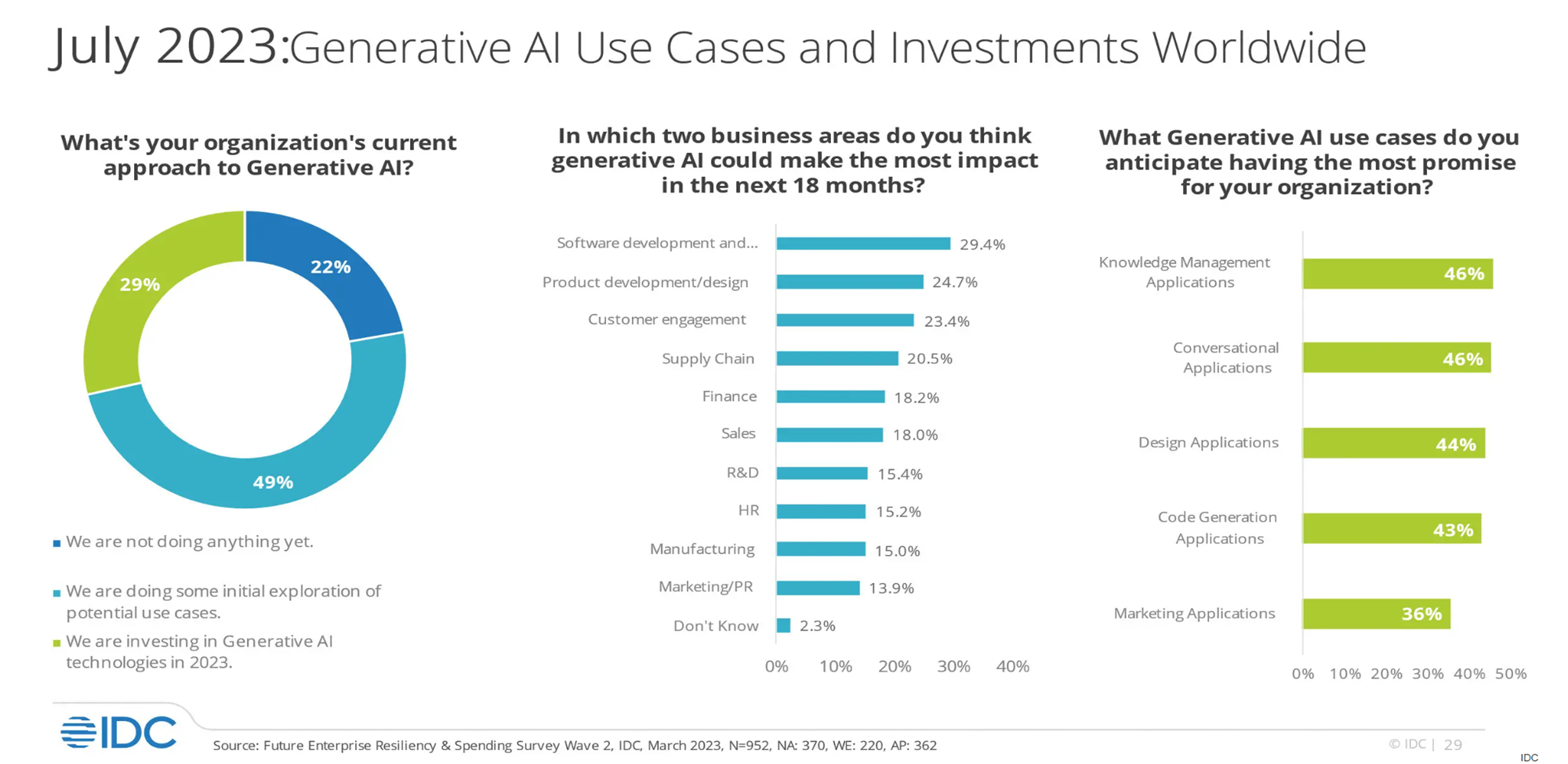
The survey reveals that approximately 78% of organizations are either already using Generative AI or actively exploring its applications. This number is likely higher now due to its time-saving benefits. Ask your colleagues or friends—many likely use AI tools for coding, writing, generating images, or creating videos to complete tasks more efficiently.
The blue bars in the middle illustrate fields significantly transformed by Generative AI. Software development leads the way, as Generative AI leverages open-source projects to improve coding capabilities. Product development follows, where LLMs help analyze vast data sets to design superior products. Personally, I often use Generative AI to enhance document structures, ensuring completeness and clarity.
Regulated Generative AI
Generative AI’s widespread adoption has also raised concerns. For instance, OpenAI’s ChatGPT—while immensely popular—has faced scrutiny for generating inappropriate responses or handling sensitive information poorly, causing businesses to ban its use in workplaces.
Despite these challenges, Generative AI remains a commercial trend. To meet enterprise needs, “regulated Generative AI” is crucial, ensuring responsible and appropriate usage in business scenarios.
Diverse LLMs in Generative AI
Over the years, both commercial and open-source LLMs have proliferated, reflecting significant investment in Generative AI. Let’s explore some popular LLMs:
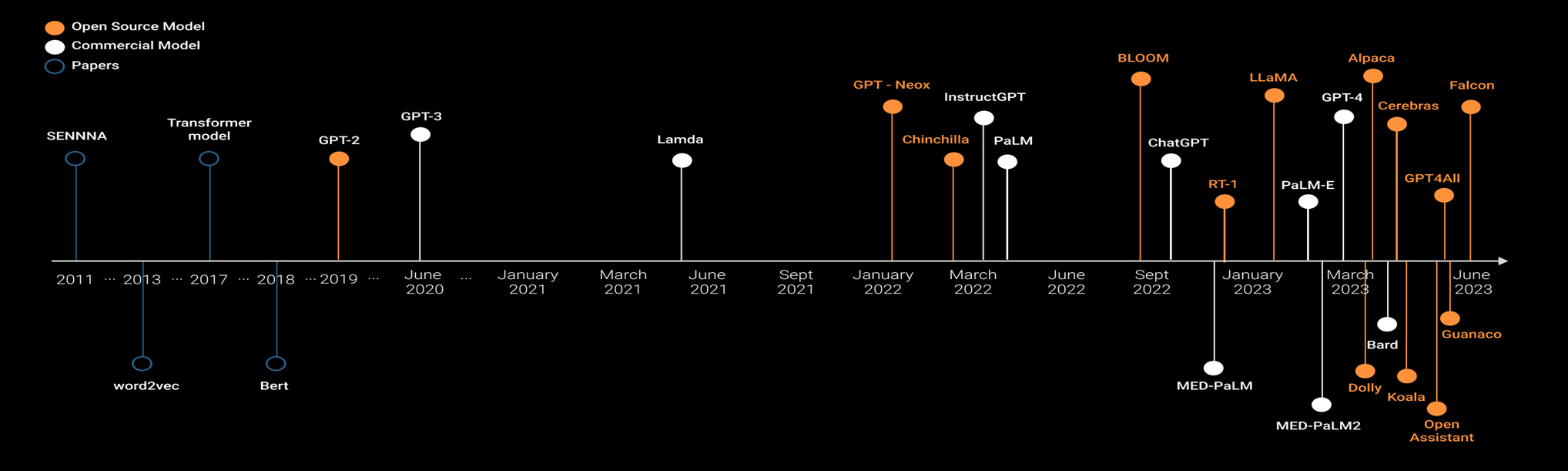
- GPT Models
OpenAI’s GPT models, including the widely recognized ChatGPT and the recently launched GPT-4, have garnered substantial interest in the AI community. These proprietary models require licensing fees and impose usage restrictions.
- LLaMA 2
Developed by Meta, LLaMA 2 is an open-source LLM designed to advance research in the field. Its various configurations, ranging from 7 to 65 billion parameters, allow access to LLMs with reduced computational requirements.
- PaLM 2
PaLM 2, Google’s next-generation LLM, builds on its AI research and was unveiled during the 2023 I/O keynote.
- Claude v2
Developed by Anthropic in partnership with AWS, Claude v2 features a "Constitutional AI" training approach aimed at creating safe, user-friendly systems.

In summary, GPT-4 excels in consumer-facing applications but incurs high costs, while Claude v2 stands out in regulated environments, offering transparency and safety. Similarly, LLaMA 2 and PaLM 2 prioritize efficiency and resource optimization, catering to diverse business needs.
Claude AI Overview
Claude’s "Constitutional AI" is designed to adhere to principles of helpfulness, honesty, and harmlessness, ensuring accurate, unbiased interactions. This approach makes Claude particularly suitable for sensitive or high-stakes business applications.
AWS Bedrock
AWS Bedrock simplifies building and deploying LLMs by offering pre-trained models, integration with AWS services, and robust data security.
AI in Business Applications
AI’s business impact spans customer experience enhancement, productivity boosts, and operational improvements. For example, chatbots and virtual assistants provide personalized support, while Generative AI aids in document analysis and workflow optimization.
Conclusion
We hope this overview of Generative AI and Bedrock inspires you to explore AI’s potential in your business. For tailored solutions or to unlock more value with LLMs, feel free to contact Netron Information Technology. See you next time!
Exploring Generative AI and Bedrock
We’re excited to share insights into the features of Generative AI and Bedrock today, along with ways they can be applied to business services.
As an IT professional, I’m thrilled about AWS’s introduction of this service. In the early days, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) had steep barriers to entry. Understanding various AI frameworks, acquiring domain knowledge, and handling data collection and processing were daunting tasks requiring significant resources. Without ample time and manpower, these technologies felt out of reach.
Now, AWS Bedrock simplifies everything. With just API calls, we can achieve amazing results! It’s hard not to exclaim, “This is incredible!” Let’s dive into an overview to understand how it all works. Without further ado, let’s begin exploring!
Generative AI Trends and Large Language Models (LLMs)
The Future of AI Is Now
Before diving into the details, allow me a quick retrospective. Early digital transformation primarily focused on infrastructure upgrades—for example, moving on-premise systems to the cloud, implementing containerization, or integrating DevOps into workflows. However, the most significant game-changer has been Generative AI.
According to research, 95% of business analysts now view AI as critical to digital transformation. Additionally, 80% of organizations report utilizing AI in their business activities or production processes. It’s clear that AI adoption will continue to grow, revolutionizing enterprise workflows. Furthermore, 81% of businesses reported a positive return on investment within two years of implementing AI, highlighting its value in driving commercial outcomes.
AI Use Cases and Investment
Let’s look at findings from an IDC survey conducted in July:

The survey reveals that approximately 78% of organizations are either already using Generative AI or actively exploring its applications. This number is likely higher now due to its time-saving benefits. Ask your colleagues or friends—many likely use AI tools for coding, writing, generating images, or creating videos to complete tasks more efficiently.
The blue bars in the middle illustrate fields significantly transformed by Generative AI. Software development leads the way, as Generative AI leverages open-source projects to improve coding capabilities. Product development follows, where LLMs help analyze vast data sets to design superior products. Personally, I often use Generative AI to enhance document structures, ensuring completeness and clarity.
Regulated Generative AI
Generative AI’s widespread adoption has also raised concerns. For instance, OpenAI’s ChatGPT—while immensely popular—has faced scrutiny for generating inappropriate responses or handling sensitive information poorly, causing businesses to ban its use in workplaces.
Despite these challenges, Generative AI remains a commercial trend. To meet enterprise needs, “regulated Generative AI” is crucial, ensuring responsible and appropriate usage in business scenarios.
Diverse LLMs in Generative AI
Over the years, both commercial and open-source LLMs have proliferated, reflecting significant investment in Generative AI. Let’s explore some popular LLMs:

- GPT Models
OpenAI’s GPT models, including the widely recognized ChatGPT and the recently launched GPT-4, have garnered substantial interest in the AI community. These proprietary models require licensing fees and impose usage restrictions.
- LLaMA 2
Developed by Meta, LLaMA 2 is an open-source LLM designed to advance research in the field. Its various configurations, ranging from 7 to 65 billion parameters, allow access to LLMs with reduced computational requirements.
- PaLM 2
PaLM 2, Google’s next-generation LLM, builds on its AI research and was unveiled during the 2023 I/O keynote.
- Claude v2
Developed by Anthropic in partnership with AWS, Claude v2 features a "Constitutional AI" training approach aimed at creating safe, user-friendly systems.
In summary, GPT-4 excels in consumer-facing applications but incurs high costs, while Claude v2 stands out in regulated environments, offering transparency and safety. Similarly, LLaMA 2 and PaLM 2 prioritize efficiency and resource optimization, catering to diverse business needs.
Claude AI Overview
Claude’s "Constitutional AI" is designed to adhere to principles of helpfulness, honesty, and harmlessness, ensuring accurate, unbiased interactions. This approach makes Claude particularly suitable for sensitive or high-stakes business applications.
AWS Bedrock
AWS Bedrock simplifies building and deploying LLMs by offering pre-trained models, integration with AWS services, and robust data security.
AI in Business Applications
AI’s business impact spans customer experience enhancement, productivity boosts, and operational improvements. For example, chatbots and virtual assistants provide personalized support, while Generative AI aids in document analysis and workflow optimization.
Conclusion
We hope this overview of Generative AI and Bedrock inspires you to explore AI’s potential in your business. For tailored solutions or to unlock more value with LLMs, feel free to contact Netron Information Technology. See you next time!