Through Netron’s cloud migration service, accelerate your cloud adoption by migrating your infrastructure and applications to AWS without disrupting your business.
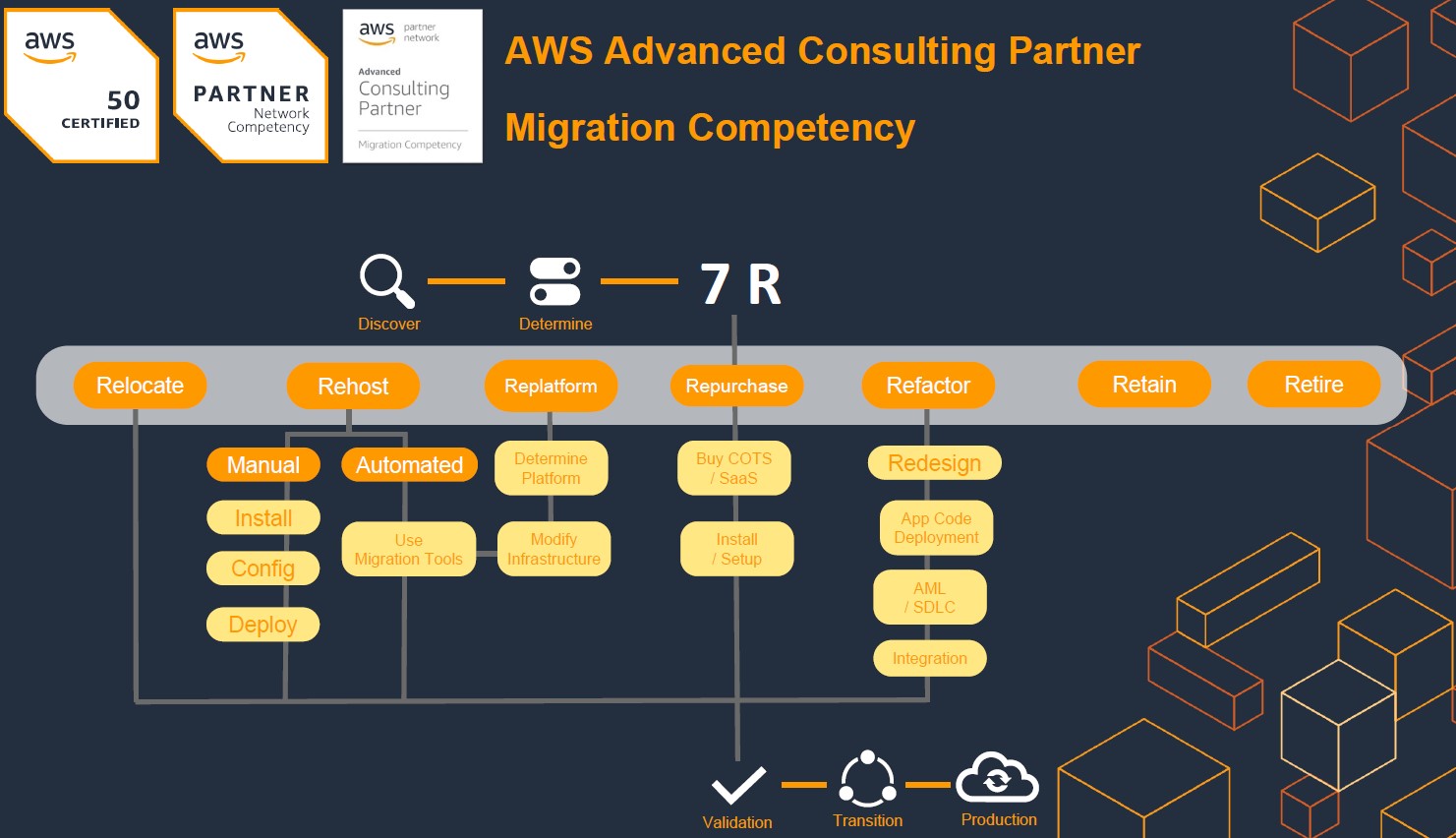
The universal strategies for Cloud migration summarized in 7 R’s
Seven common migration strategies for moving applications to the cloud. These strategies build upon the 5 Rs that Gartner identified in 2011 and consist of the following:
- Refactor/re-architect – Move an application and modify its architecture by taking full advantage of cloud-native features to improve agility, performance, and scalability. This typically involves porting the operating system and database. Example: Migrate your on-premises Oracle database to the Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition.
- Replatform (lift and reshape) – Move an application to the cloud, and introduce some level of optimization to take advantage of cloud capabilities. Example: Migrate your on-premises Oracle database to Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) for Oracle in the AWS Cloud.
- Repurchase (drop and shop) – Switch to a different product, typically by moving from a traditional license to a SaaS model. Example: Migrate your customer relationship management (CRM) system to Salesforce.com.
- Rehost (lift and shift) – Move an application to the cloud without making any changes to take advantage of cloud capabilities. Example: Migrate your on-premises Oracle database to Oracle on an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance in the AWS Cloud.
- Relocate (hypervisor-level lift and shift) – Move infrastructure to the cloud without purchasing new hardware, rewriting applications, or modifying your existing operations. This migration scenario is specific to VMware Cloud on AWS, which supports virtual machine (VM) compatibility and workload portability between your on-premises environment and AWS. You can use the VMware Cloud Foundation technologies from your on-premises data centers when you migrate your infrastructure to VMware Cloud on AWS. Example: Relocate the hypervisor hosting your Oracle database to VMware Cloud on AWS.
- Retain (revisit) – Keep applications in your source environment. These might include applications that require major refactoring, and you want to postpone that work until a later time, and legacy applications that you want to retain, because there’s no business justification for migrating them.
- Retire – Decommission or remove applications that are no longer needed in your source environment.
Netron’s migration methnology
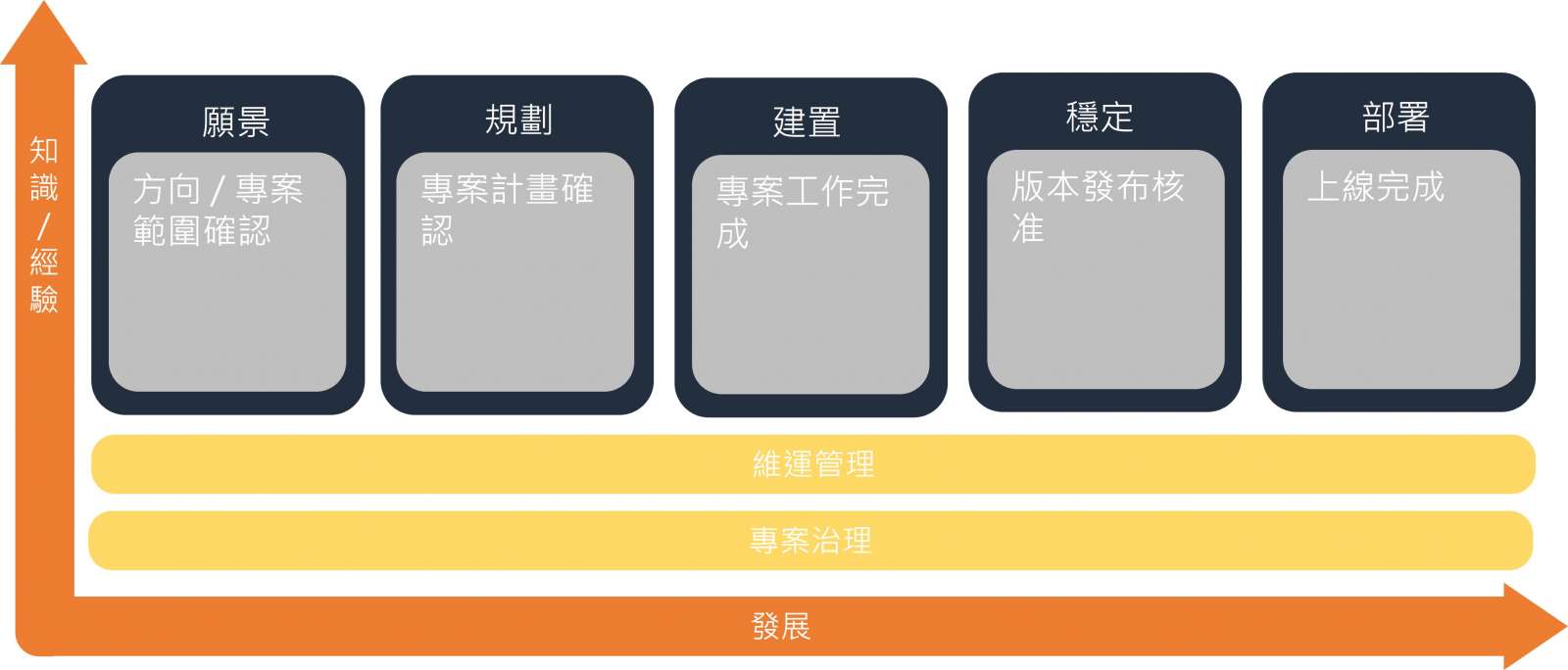
Vision: include establishing a business vision and defining the scope of work required to achieve it (e.g., justifying the business case, conducting business research, etc.)
Planning: The planning phase covers everything from developing detailed functional requirements, system and application architectures, user interface prototypes, and even detailed project plans for the rest of the project
Build: The build phase begins with the first generation of development and ends with the "feature completion" milestone (Alpha or Beta release)
Stabilization: unit testing and functional acceptance
Deployment: transfer the project to operations and support, and acquire final customer approval for the project.
After going on Cloud, you can achieve
Cost optimization
High expandability, usability
raised business flexibility
Enhanced operational elasticity



